As of 2023, global digital advertising spending reached $681 billion compared to $549 billion in 2022, accounting for nearly 70% of total worldwide ad spending. As brands increase their investment in online campaigns, retailers must optimize their platforms to showcase ads and gain a competitive edge.
At the heart of this optimization are ad tags. These codes are the backbone of online advertising, enabling the delivery of ads to the right audience at the right time. By effectively managing ad tags, you can maximize your advertising ROI and drive business growth.
This blog explores different aspects of ad tags and how they enhance ad-serving efficiency in large-scale campaigns.
What are Ad Tags?
An ad tag, also known as a ‘placement tag’ or a ‘creative tag’, is a snippet of HTML or JavaScript code included in the source code of a webpage. When a visitor loads a webpage on which an ad tag has been placed, it triggers the display of a specific ad. This code also guides the publisher’s ad server in placing a particular ad at a specific location on a page.
Ad tags are an integral part of the digital advertising ecosystem as they store information related to ad requirements, such as format, category, and dimensions. They work in the background so that appropriate ads are delivered to the intended audience precisely when needed.
Process of Ad Tags in Ad Serving
Ad tags contain information like the destination URL, ad creative, and different tracking parameters. When you embed these tags into your webpage’s HTML code, they ensure seamless communication between the ad server and your website.
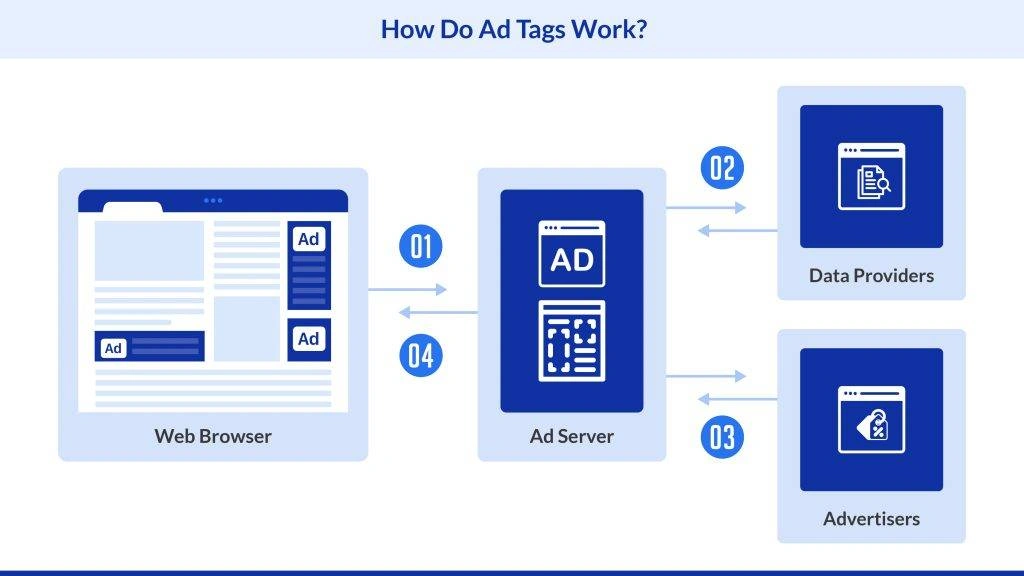
Here is a brief overview of the process of ad tags in serving advertisements:
- Activation: The ad tag triggers as soon as the user visits the webpage.
- Request: The web browser then initiates a request to the designated ad server that is the central repository for your advertisements.
- Selection: The ad server analyzes various factors, including user demographics and browsing data, to identify the most relevant ad for the specific visitor.
- Delivery: The server then instantly creates and delivers the chosen ad content for display on your webpage. This entire process typically occurs within milliseconds, ensuring a smooth user experience.
Ad tags are also valuable data collection tools as they feature tracking systems to monitor user interactions, like clicks and impressions. You can leverage this data to understand how users respond to your ads and refine campaigns for better performance and targeted reach.
Types of Ad Tags
Here are different types of ad tags that can be used in various ad campaigns:
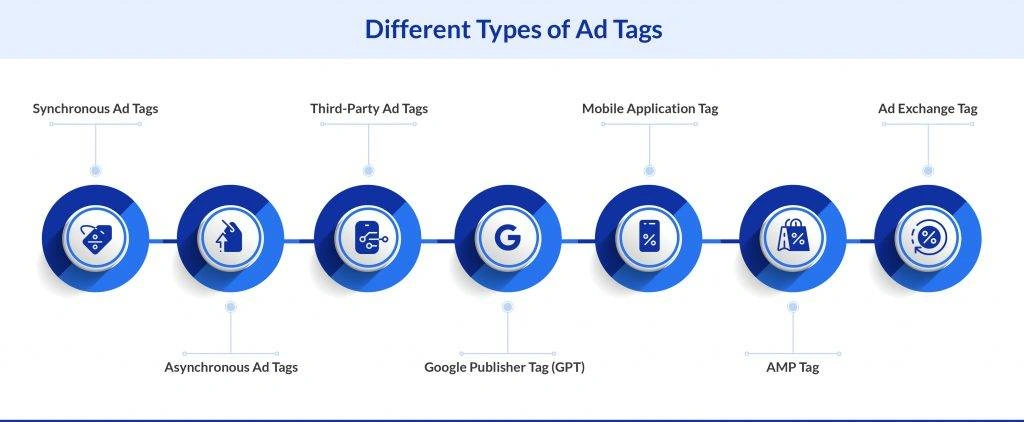
Synchronous Ad Tags
These ad tags load together with the rest of the webpage. This ensures that the advertisements are seen as soon as the page loads. However, if synchronous tags face any rejection or encounter a snag, they can reduce the overall loading speed of your site, affecting the user experience.
Asynchronous Ad Tags
These tags load independently from your webpage, ensuring that the user’s interaction with your site remains uninterrupted and fluid. The loading speed of the ad itself will not affect the website’s overall performance. Asynchronous tags allow the webpage to load normally, even if the ad encounters an error.
Third-Party Ad Tags
These tags are useful in gathering detailed insights on ad performance and engagement. They allow for real-time adjustments and targeting, enhancing the reach of your ads. Incorporating third-party ad tags into the website improves the precision and effectiveness of your campaigns.
Google Publisher Tag (GPT)
Developed by Google specifically for their advertising platforms, GPT enables dynamic ad request building. This allows for advanced ad management and supports publishers in building ad requests dynamically. These ad tags enhance the targeting and optimization capabilities of your campaigns when using Google Ad Manager.
Mobile Application Tag
These ad tags are specifically designed for the mobile app environment. They ensure that different ads are displayed seamlessly within various mobile applications. Their specialized nature allows for customized ad delivery, boosting your reach and engagement with users who are actively using the mobile apps.
AMP Tag
These tags are meant for Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP). They improve the loading speed of ads on mobile pages, ensuring that the content is delivered quickly. With AMP tags, you can enhance the mobile browsing experience, supporting smoother and more engaging user interactions with your ads.
Ad Exchange Tag
Ad exchange tags play an important role in programmatic advertising to facilitate the buying and selling of online ad inventory. These tags connect advertisers directly to a vast network of publishers through ad exchanges, enabling real-time bidding for efficient ad placement.
Components of Ad Tags
Here is the breakdown of the typical ad tag structure:
- Base URL: This initial part of the ad tag specifies the ad server that will deliver the ad. (For example, http://ad.server.com/..?..)
- Parameters: The question mark (?) indicates the start of parameters that provide specific instructions for the ad. These parameters come in key-value pairs separated by semicolons (;).
Here are the components you can use as parameters in the ad tag:
- Ad Request Code: After the URL, some ad tags can include a code that identifies the type of ad request.
- Publisher ID: This section identifies your website or app as the ad publisher.
- Zone/Channel: The zone defines a designated area on the publisher’s website for displaying ads.
- Targeting Criteria: Some ad tags allow you to include parameters like topics, subtopics, and keywords. They specify the demographics or interests.
- Ad Slot: This helps differentiate between multiple ad zones with the same dimensions.
- Ad Size: This part specifies the optimal dimensions in pixels for the displayed ad.
- Unique Identifier: It helps generate a unique value for each ad request, aiding in tracking and billing.
How Does Ad Tech Collaboration Work?
Here is a brief overview of how ad tech collaboration takes place between different parties:
Publishers
Publishers are the owners of media spaces where ads are displayed. They utilize ad tags to manage and control the ads displayed on their sites. For instance, as a publisher for your retail platform, you can use ad tags to determine which ads will be displayed.
Advertisers
On the other side of the spectrum are the retail advertisers who create and supply ads. For advertisers, ad tags serve as a tracking tool, enabling monitoring of ad performance and gathering valuable data. This data is then used to optimize the ad campaigns to achieve desired goals.
Ad Networks
Ad networks act as the bridge between publishers and advertisers. They use ad tags to ensure the right ads reach the target audience at the right time. This precision targeting helps enhance the effectiveness of the ads and ensures a better return on investment for advertisers.
Data Management Platforms (DMPs)
DMPs collect data from various sources and then analyze it. Ad tags help them offer useful insights to advertisers and publishers for optimizing ad performance and delivering engaging ad content.
Additional Read: Retailers Guide To Ad Tech, All You Need To Know
The Future of Ad Tags
Emerging technologies are transforming the way ad tags are used. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is enabling more personalized ads, tailoring content to individual users for a more engaging experience. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are creating immersive experiences that captivate consumers and drive deeper engagement. For instance, a retail marketplace like Flipkart can use tags to deliver AR and VR-powered ads for products such as footwear or cosmetics.
Evolving privacy regulations are also making a significant impact on the advertising industry. The reduction of third-party cookies and the introduction of new data privacy regulations, such as the California Privacy Rights Act, are reshaping the ad tech landscape. These changes are forcing businesses to rethink their strategies and find new ways to use ad tags while respecting user privacy effectively. Also, there is a shift towards the use of first-party data in advertising.
Changes in consumer behavior will also have an impact on the future of ad tech. Consumers are demanding more authenticity and social responsibility from brands. This shift toward more personalized and contextual ad experiences is affecting ad-serving efficiency, pushing the industry to innovate and adapt.
Enhance Your Ad Serving Efficiency with Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC)
As a retailer, you must optimize your website to maximize ad-serving efficiency and leverage ad tags strategically. This is where retail tech platforms like FCC come into the picture with a suite of tools tailored to meet the evolving needs of retailers. From real-time analytics to advanced targeting capabilities, FCC allows you to make data-driven decisions and streamline ad performance with its Ads Manager.
The FCC Ads Manager enables you to capitalize on every customer interaction, foster deeper engagement with brands, and drive meaningful conversions. It serves as a comprehensive platform for building a robust sponsored ads ecosystem. With the ability to launch retail platform ads, you can swiftly generate additional revenue streams, enhance brand interaction on your platform, and monetize all online activities through sponsored listings.
The FCC Ads Manager is equipped with cutting-edge ad-tech features to help implement attractive ad revenue models. It supports multiple ad formats, including video ads, rich media, and static ads, offering a comprehensive solution for all your advertising needs.
It’s time to take your ad performance to the next level.
Get started with FCC Ads Manager today and experience the difference it can make to your retail business.