Strategic pricing is often an important tool for retailers to build a strong customer base and maximize their revenue potential. One such pricing method that has been successful in the retail sector is price skimming. It involves launching a product at a premium, then gradually reducing it over time, skimming maximum value at each stage.
This strategy is particularly effective for unique and innovative products, where early adopters are willing to pay a higher price for novelty. However, successfully implementing price skimming requires thorough planning and deep knowledge of the prospective audience.
This blog covers the key aspects of price skimming, including its benefits, challenges, strategic implementation, and real-world examples.
What is the Price Skimming Strategy?
How Does the Price Skimming Strategy Work?
Price skimming focuses on creating a sense of urgency amongst your target customers, creating an ‘I-must-have-it’ mindset. This price strategy is used in mature markets where customers possess two key traits: the financial capability and the desire to acquire the latest products as soon as they are available.
Under price skimming, you start by setting a high initial price to reflect the perceived value of your product. Early adopters, those who value innovation and are willing to pay a premium for it, are your initial target market. They perceive your high price as an indicator of superior quality and exclusivity and are willing to pay for it. This allows you to quickly recover your investment and generate substantial initial revenue.
As the product matures in the market, you gradually reduce the price. This is not a sign of desperation or absence of high consumer demand. Instead, it is a strategic move to attract a wider audience. As the price drops, a new segment of the market, which was initially interested but discouraged by the high price, now finds the product within its reach. This allows you to continue generating revenue at a lower margin but from a larger customer base.
Let’s understand the workings of price skimming with the help of this graph. Here, the y-axis represents the price, and the x-axis represents the quantity.
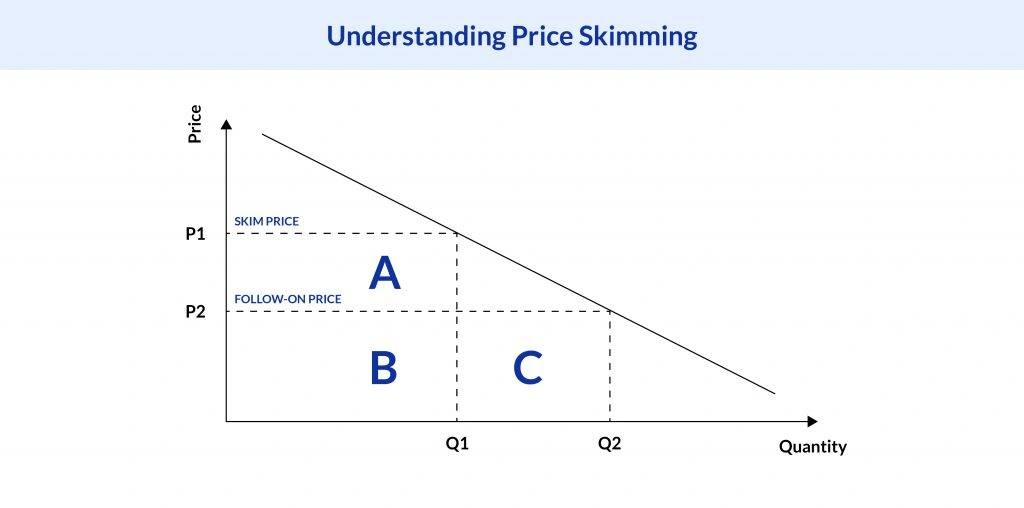
The graph depicts a downward-sloping line, indicating a negative relation between quantity and price, which is a fundamental concept in economics.
- Skim Price (P1): At the product’s launch, the price is at its highest point on the y-axis, labeled as P1. This is the ‘Skim Price’. At this price, the quantity sold is at Q1, marked as point A on the graph. This phase targets early adopters who value innovation and are willing to pay a premium for it. They perceive the high price as an indicator of superior quality and exclusivity. This allows the company to recover its investment and generate substantial initial revenue quickly.
- Follow-on Price (P2): As the product matures in the market, the price is gradually reduced to P2, labeled as the ‘Follow-on Price’. This is not a sign of desperation or a lack of demand. Instead, it’s a strategic move to attract a wider audience. As the price drops to P2, the quantity sold increases from Q1 to Q2, moving from point B to point C on the graph. This new segment of the market, which was initially interested but discouraged by the high price, now finds the product within its reach. This allows the company to continue generating revenue at a lower margin but from a larger customer base.
Real-World Example of Price Skimming Strategy?
Here are the examples of companies that have effectively employed the price skimming strategy.
Apple iPhone
Apple’s iPhone series is a prime example of successful price skimming in the smartphone market. Each new iPhone model is launched at a premium price point, typically ranging from $799 for the base model to over $1,599 for the top-tier variant. Apple targets early adopters and tech enthusiasts who are willing to pay a premium for the latest features and brand exclusivity. As the product matures and newer models are released, prices at Apple Stores gradually decrease to attract a broader customer base. For instance, the iPhone 15, was initially priced at $799 at the time of its launch in 2023, but it is available for around $699 as of May 2024, making it more accessible to price-sensitive consumers.
Samsung Galaxy
Samsung’s Galaxy smartphone lineup is another prime example of successful price-skimming implementation. Similar to Apple, Samsung targets early adopters and tech enthusiasts who are willing to pay a premium for the latest features and brand exclusivity. The company’s flagship models, such as the Galaxy S series, are introduced at high prices to capitalize on the initial demand from early adopters. For example, the Galaxy S22 Ultra was launched at a starting price of $1,199, targeting consumers who value the latest technology and are willing to pay a premium for it. As newer models are released and the product cycle progresses, Samsung gradually reduces prices to maintain its market share and engage a wider customer base. The Galaxy S21, initially priced at $999 at the time of its launch in January 2021, is available for around $699 as of May 2024, making it affordable for mainstream users.
When Should You Use a Price Skimming Pricing Strategy?
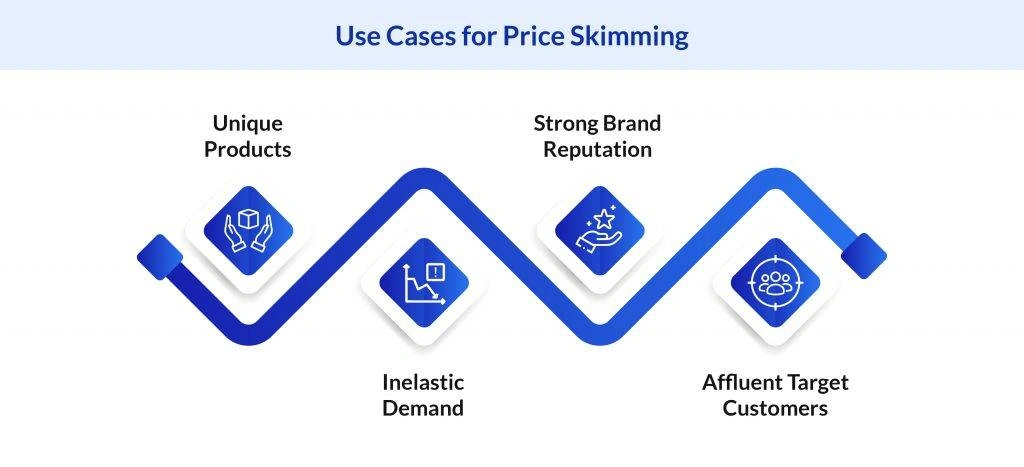
Similar to other pricing strategies, skim pricing is effective only when specific conditions are satisfied, such as having unique products, inelastic demand, a robust brand reputation, and financially capable customers. Here are the different situations in which you can use this method:
Unique Products
A price-skimming strategy can be particularly effective when introducing a unique product to the market. The novelty of your product can justify premium pricing to early adopters, who are often willing to pay a higher price for the latest technology or exclusive features. By leveraging the initial excitement around your product, you can capture maximum value from the market. Then, you can gradually reduce the prices to target a wider customer base.
Inelastic Demand
Inelastic demand refers to a situation where changes in price have a minimal impact on sales volume. This is often the case for goods and services that are considered necessities or have few substitutes.
Let’s understand this concept with the help of this inelastic demand curve:
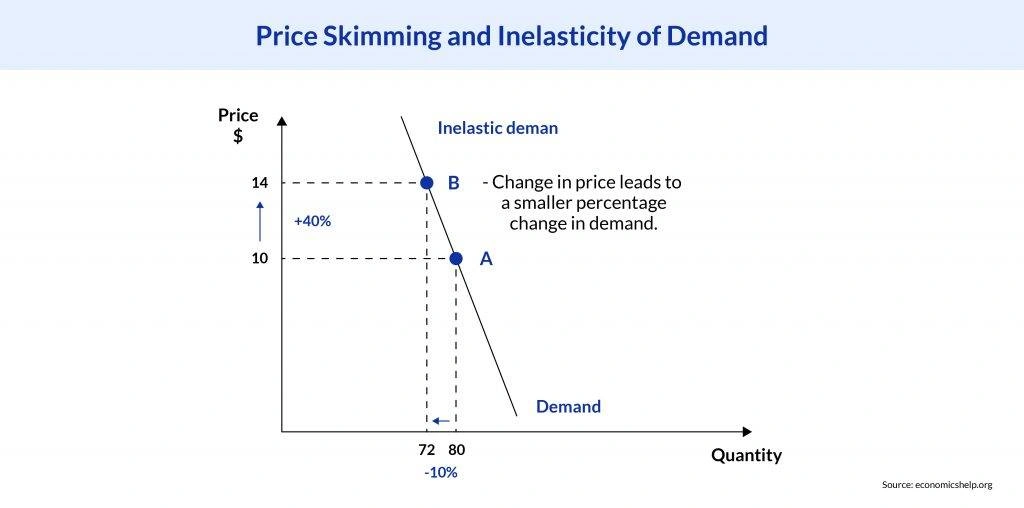
- Initial State: The initial price is $10, and the quantity demanded is 80 units. This is represented by point A on the graph.
- After Price Increase: The price increases by 40% to $14, and the quantity demanded decreases by only 10% to 72 units. This is represented by point B on the graph.
This shows that a significant increase in price (40%) results in a relatively small decrease in quantity demanded (10%), demonstrating the concept of inelastic demand.
When demand is inelastic, firms can increase prices without significantly impacting the quantity demanded. This is because consumers are less sensitive to price changes and will continue to purchase the product even at higher prices. As a result, firms can generate larger revenues and profits.
For instance, if a firm increases the price of a product by 20% and the demand decreases by only 1%, the firm’s revenue will increase because the price increase outweighs the decrease in demand. This type of pricing strategy is particularly effective for essential products or those with few substitutes, as consumers are likely to continue purchasing these products despite price increases.
Strong Brand Reputation
If your brand is known for quality, innovation, and exclusivity, customers are more likely to perceive your products as valuable and are willing to pay premium prices. By leveraging your brand equity, you can justify higher initial prices and create a perception of prestige around your new offerings. This approach allows you to capitalize on the trust and loyalty your brand has built with customers, making them more receptive to your price-skimming strategy.
Affluent Target Customers
Affluent individuals often value exclusivity, status, and the latest trends, making them more likely to pay premium prices for new products. By setting high initial prices, you can cater to this segment of the market and create a perception of luxury and desirability around your offerings. As your product matures and newer models are released, you can gradually reduce prices to attract a broader customer base while still maintaining a premium positioning.
The Benefits of Price Skimming Pricing Strategy
Here are the different benefits that you can enjoy through price skimming:
Achieve Quicker Return on Investment
By implementing a price skimming strategy, you can generate high initial revenue from early adopters willing to pay premium prices for your products. This revenue inflow allows you to recover your research and development costs and start generating profits sooner. The financial benefits of price skimming are useful for businesses with high fixed costs, where rapid revenue generation is crucial for profitability.
Create a Perception of Exclusivity and High Quality
By setting higher prices, you can position your products as luxurious, desirable, and of superior quality, attracting customers who value these attributes. This perception can enhance your brand image and appeal to a specific segment of the market that seeks out premium offerings. However, to maintain this perception, premium pricing must be backed by consistent quality and excellent customer service.
Implement Flexible Product Pricing
Starting with high prices to capture early adopters, you can gradually lower prices to attract a broader customer base as your product matures. This flexibility allows you to adjust to evolving market conditions, competition, and customer preferences, ensuring that your product pricing strategy remains relevant and effective. By carefully monitoring market trends and customer feedback, you can make informed decisions about when and how to adjust your prices to optimize revenue.
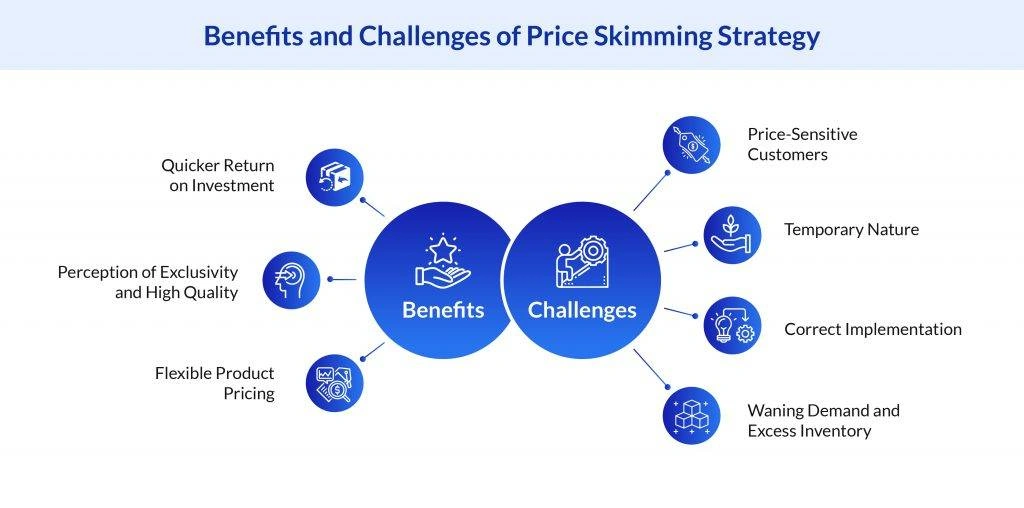
Challenges of Price Skimming Pricing Strategy
While price skimming can be a viable pricing strategy, it also presents several challenges that you must navigate. Understanding and addressing these issues is crucial for the long-term success of your pricing approach.
Attracting Price-Sensitive Customers
One of the primary challenges of price skimming is managing the expectations and potential dissatisfaction of price-sensitive customers. These customers may feel frustrated by the high initial prices, perceiving them as unfair or exclusionary. To mitigate this issue, communicate your product’s value proposition clearly. This will help you highlight the distinct features of your offerings and benefits that justify the premium pricing.
Managing Temporary Nature
The price skimming strategy is inherently temporary, as businesses must eventually lower prices to maintain market competitiveness. This transition can be challenging, as you need to carefully plan and execute price reductions to avoid alienating early adopters or losing market share to competitors. Effective communication, strategic timing, and a well-designed pricing roadmap are crucial to ensure a smooth transition.
Ensuring Correct Implementation
Retailers must carefully execute their pricing approach, market positioning, and communication to ensure optimal results. Pricing execution requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, customer preferences, and competitive landscape. Clear and transparent communication with customers is essential to manage expectations and build trust throughout the product’s life cycle.
Mitigating Waning Demand and Excess Inventory
As prices gradually decrease, customers may delay purchases, anticipating further reductions. This can result in a buildup of unsold stock, tying up capital and storage space. To mitigate this challenge, you must accurately forecast demand and adjust prices accordingly through effective inventory management systems powered by data analytics.
Combining Price Skimming with Other Pricing Strategies
Conclusion
- FCC Pricing Manager offers end-to-end price management to improve margins and GMV across categories. It enables you to automate your pricing decisions with robust AI-based algorithms built over 14+ years and used by dozens of leading retailers and brands worldwide.
- FCC Assortment Manager provides advanced selection data analysis to enhance your catalog and grow your revenue. It helps you benchmark your selection against the competition and identify new product selection trends.
- Competitive Intelligence is an AI-based tool that provides a 360-degree analysis of all your competitors across sales channels. It allows you to track their products, pricing and demand across all channels and gives you a strategic edge by helping you stay one step ahead of the competition.
- Digital Commerce Engine offers a comprehensive e-commerce solution for brands like you. It allows you to launch your e-commerce Marketplace and elevate your customer experience through the world-class tech stack of e-commerce giant Flipkart.