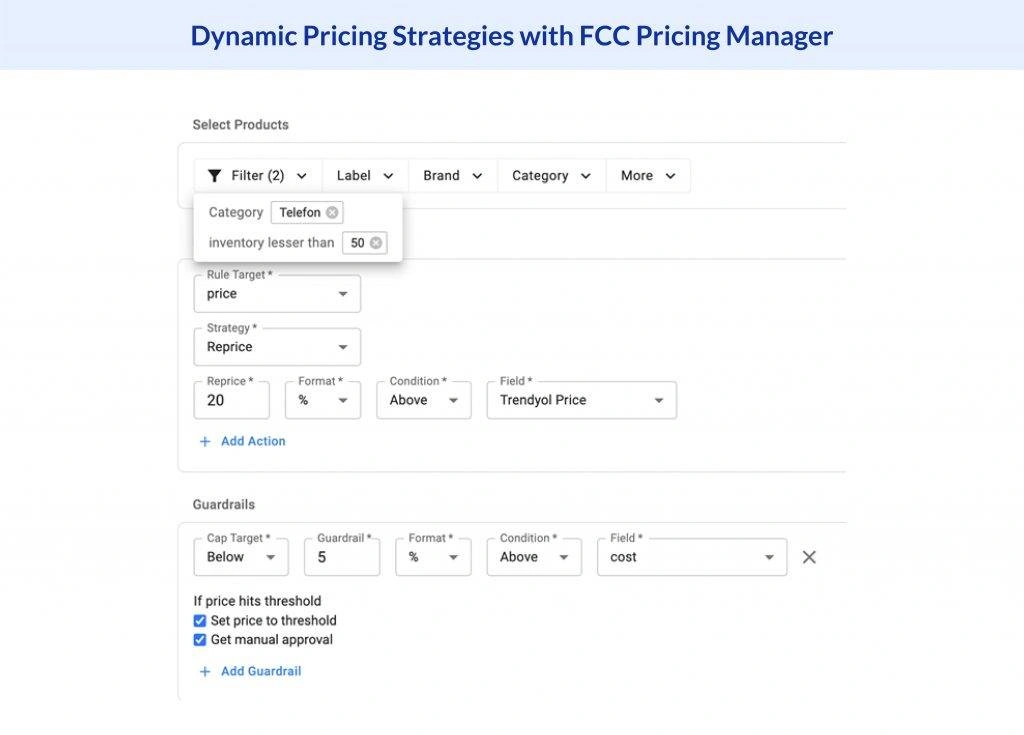
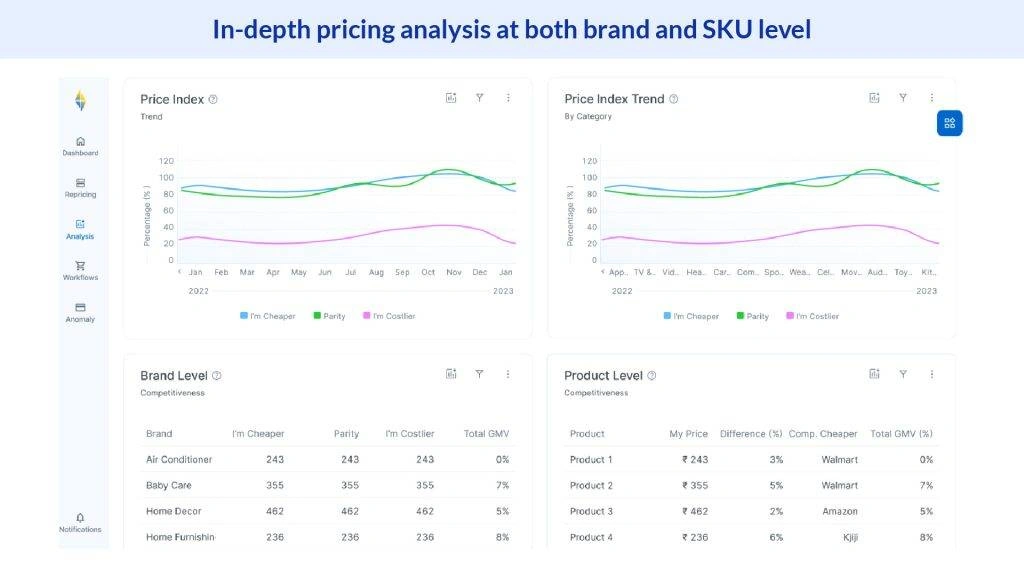
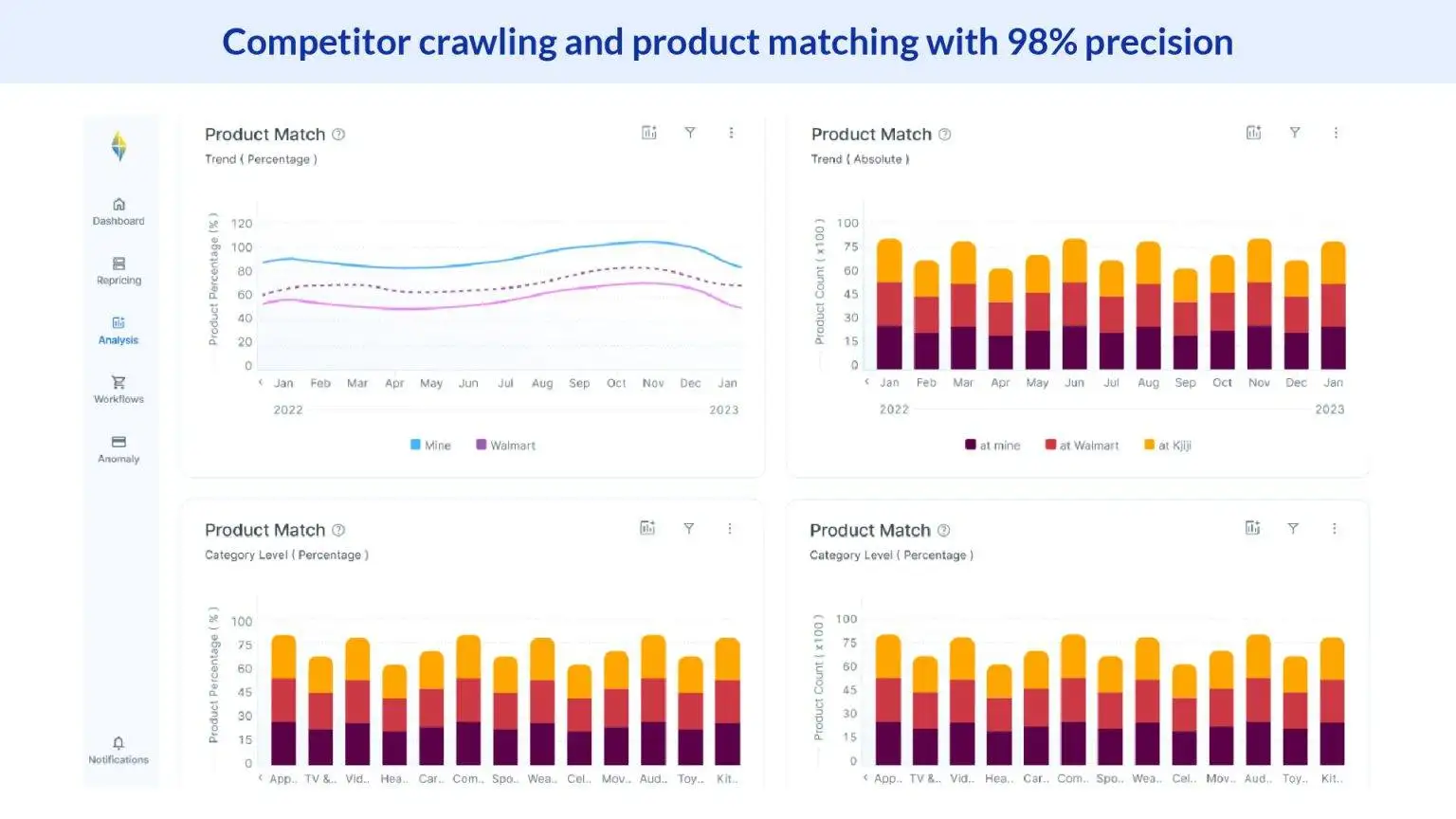
FAQ
Another name for high-low pricing is promotional pricing. It can also be referred to as discount pricing or price skimming in certain contexts, depending on the specific approach.
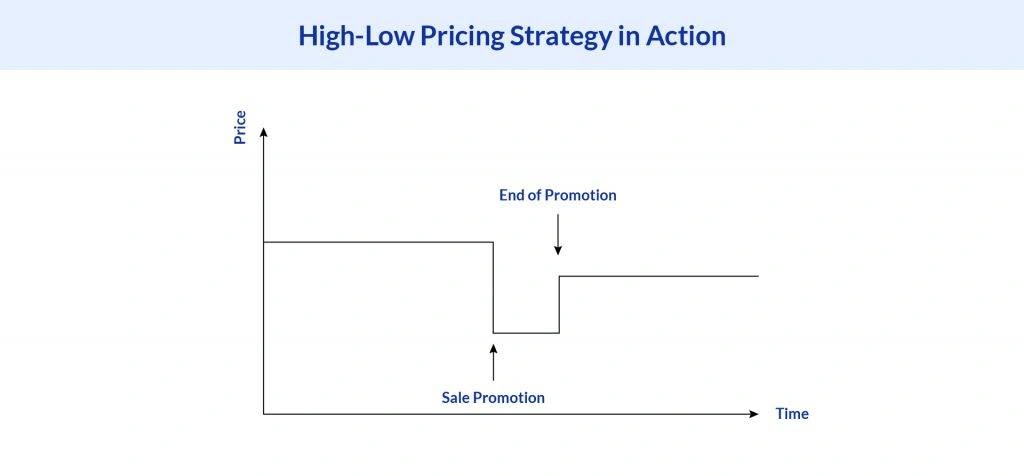
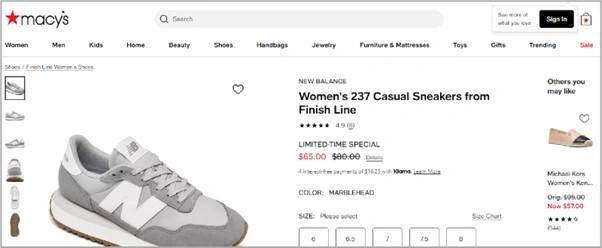
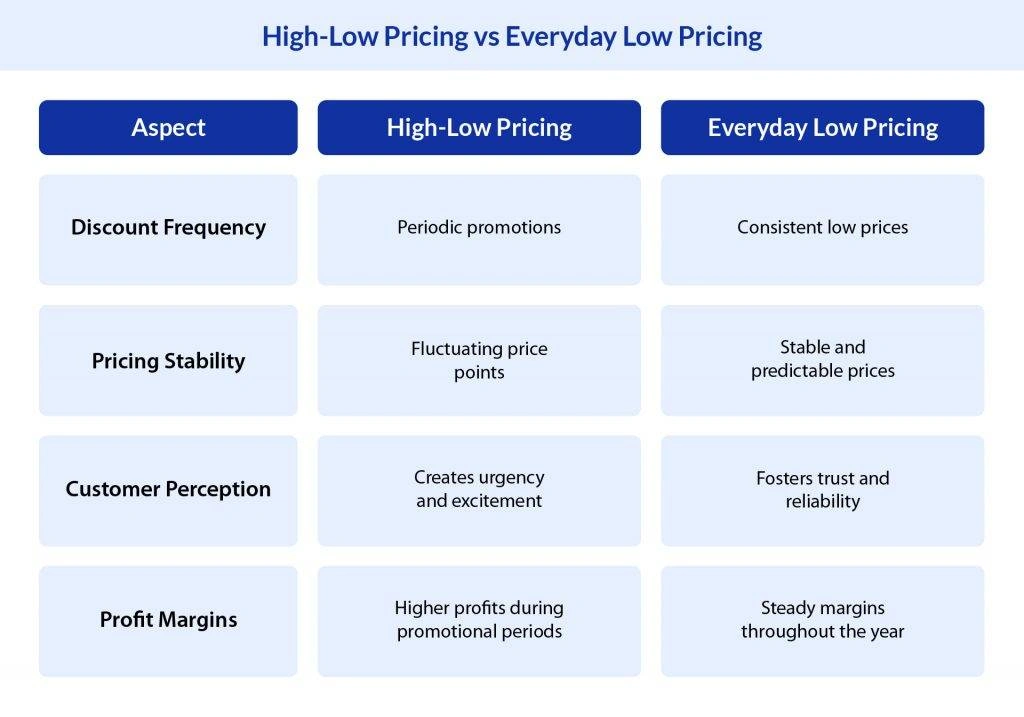
A high-low pricing tactic is a pricing strategy where a product is initially priced high but is later offered at a discounted price for a limited period. Retailers typically use this strategy to drive traffic and create urgency for customers to buy before prices return to their original, higher levels. This tactic often involves regular promotions, sales events, and seasonal discounts to attract customers who are motivated by deals.
A high-quality low-price strategy is a marketing approach where a company offers high-quality products at prices lower than competitors, aiming to create value for customers by providing quality at an affordable cost. This strategy seeks to build customer loyalty and increase market share, often by differentiating the brand on quality and value rather than solely on price.
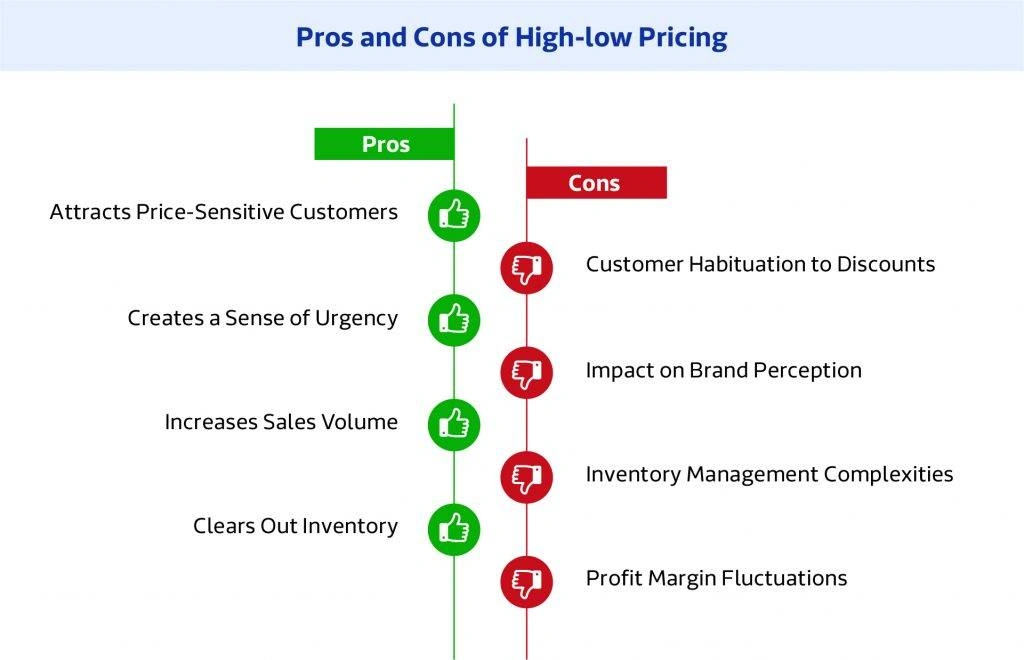
A high-low pricing strategy can be beneficial by creating a perception of premium value when products are initially priced higher, which attracts customers seeking quality or exclusivity. Over time, offering discounts or sales can incentivize price-sensitive buyers, boosting sales during promotional periods. Additionally, this strategy helps retain customers by providing opportunities for future purchases, catering to both those willing to pay full price and those waiting for lower prices.
The Hi-Lo pricing sequence refers to the cycle where a retailer sets high initial prices for products and then offers them at lower prices through discounts or promotional offers over time. The sequence typically involves a high initial price, followed by a discount phase during sales events or limited-time promotions, and finally a price return to its original high level. This sequence allows businesses to maximize revenue by attracting different customer segments at various price points.
The high-low price indicator is a metric used by retailers to track the difference between the regular price and the discounted price of products. It helps to measure the effectiveness of the high-low pricing strategy by showing how much discount was offered and how often it was used, providing insight into consumer behavior and sales performance. Retailers often use this indicator to gauge whether the high-low strategy is attracting customers and generating sales, or if adjustments need to be made.
More Blogs
See how retailers and brands are winning with FCC

Everything About Price Skimming Strategy Explained
Read More
Ultimate Guide To Dynamic Pricing Strategy In 2026
Read More
Retail Pricing Strategies: Winning with Promotion Pricing in Competitive Markets
Read More
Ad Tags: Enhancing Ad Serving Efficiency in Large-Scale Campaigns
Read More
Why Retailers Should Use Pricing Comparison Engine for Growth and Better Margins?
Read More