
Evaluating 7 Best Marketplace Business Models
By Flipkart Commerce Cloud
Share On:
The vendor marketplace business model is emerging as the growth engine for the global retail sector. In fact, with a projected annual growth rate of appx. 10%, the revenue generated through retail marketplaces is set to cross $7.39 trillion by 2025. As a retailer, you might be wondering the driving force behind this impressive growth.
The answer lies in the ability of marketplace business models to cater to evolving consumer preferences in terms of variety, convenience, and competitive prices. For retailers like you, these platforms offer a chance to reach a broader audience, reduce overhead costs, and leverage data-driven insights for sustained growth. However, to enjoy success as a retail marketplace, you need to understand where your target audience spends their time and which marketplace model can help you to reach them effectively.
In this blog, let’s explore the crucial aspects of different marketplace business models and how you can select the best option for your enterprise. Keep reading to know more.
What is the Marketplace Business Model, and How Do They Make Money?
A marketplace business model is a structure that a platform uses to connect buyers and sellers. On this online platform, multiple sellers can list their products or services, and buyers can browse and purchase as per their needs.
Unlike traditional eCommerce ventures, where the company owns the inventory and sells directly to customers, marketplaces do not own the inventory. They simply provide a platform for retailers to connect with the target audience and sell their products. Marketplaces are designed to effectively cater to consumers’ demands for variety, value, and convenience, which single-seller eCommerce platforms struggle to provide.
Marketplace business models generate revenue through various strategies. The most common is the transaction fee model, where a small percentage of each transaction made on the platform is taken as a fee. Some marketplaces charge a listing fee to sellers for showcasing their products or services. Other revenue sources include commissions, subscription fees, lead fees, featured listings, and various others.
However, launching your own retail marketplace in a competitive market is not an easy task. You must start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test the marketplace idea with real users, gather feedback, and make necessary changes before going for full-scale development. This is a cost-effective way to ensure your marketplace resonates with your target audience and meets their needs effectively.
Types of Marketplaces
You can divide different marketplace business models into the following three categories:
B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
This is the most common type of marketplace where businesses sell to consumers. They offer a wide variety of products from multiple sellers, providing consumers with a one-stop shopping experience. Examples include Walmart, Flipkart, and eBay.
B2B (Business-to-Business)
In a B2B marketplace, enterprises sell products or services to other companies. These platforms often deal in bulk orders and cater to specific industries. Alibaba and ThomasNet are examples of B2B marketplaces.
C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer)
C2C marketplaces enable consumers to sell to other consumers. These platforms are often used for second-hand or handmade goods. Examples of C2C marketplaces include eBay and Etsy.
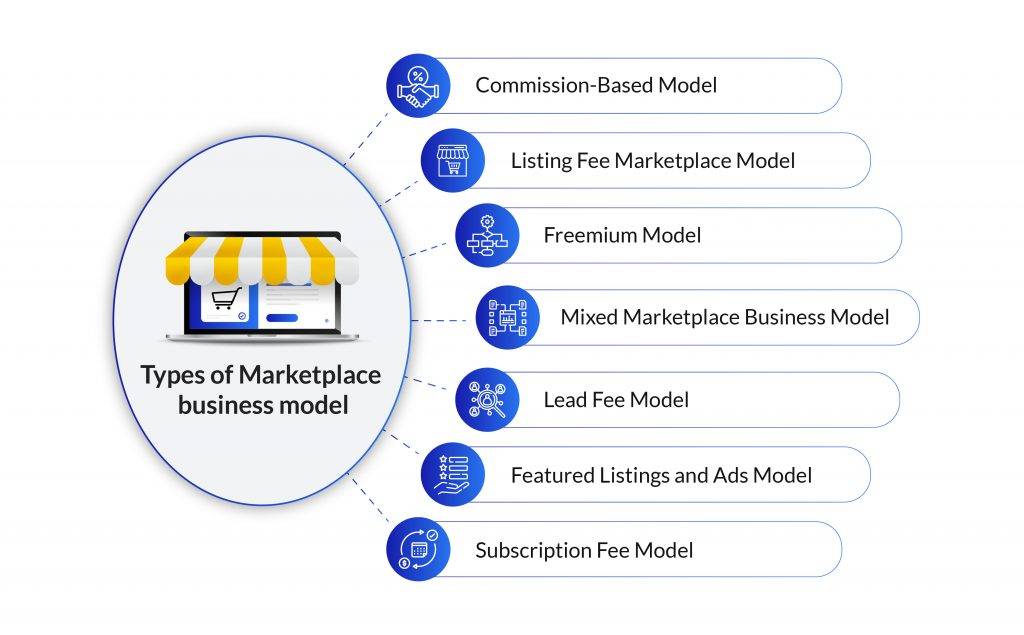
The Best Business Model for Marketplaces
Here are some of the most popular marketplace business models for your consideration.
Commission-Based Model
It is a platform where you, as the operator, charge a commission fee for every transaction. Under the commission model, this fee, often a percentage of the transaction value, is usually borne by the seller. Examples of commission-based marketplaces include Flipkart and Amazon, which charge a percentage-based fee depending on the product category.
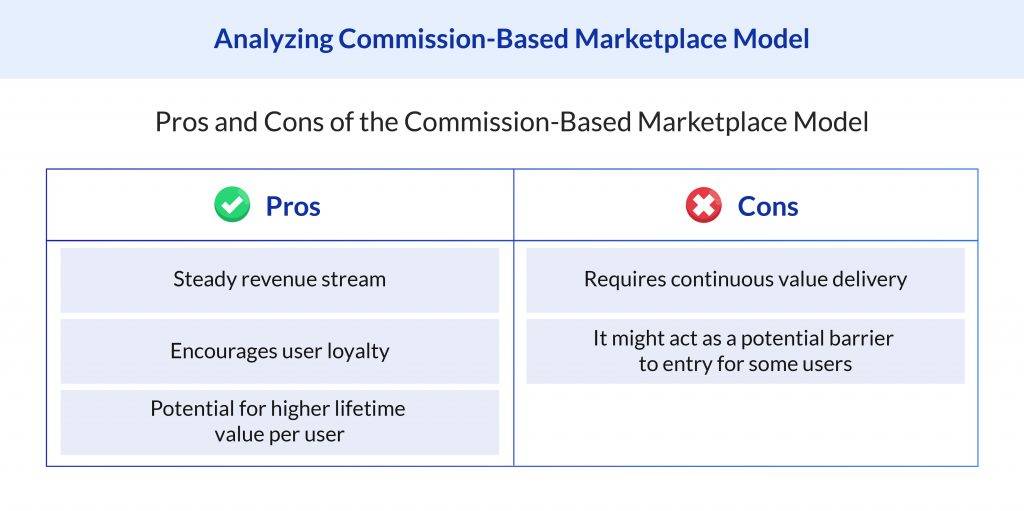
Benefits
- Alignment of Interests: Under the commission revenue model, your earnings align with the success of the sellers. The more the sellers earn, the more your marketplace earns.
- No Upfront Cost for Sellers: This encourages more sellers to join your marketplace, increasing the variety of products available for customers.
- Steady Revenue Stream: As your marketplace grows and the volume of transactions increases, so does the revenue.
Challenges
- Need for High Transaction Volume: To generate significant revenue, you need a high volume of transactions.
- Potential Seller Dissatisfaction: Sellers may be discouraged by commission rates for some product categories.
- Implementation Difficulties: Implementing a commission-based model can be challenging for certain types of products.
Suitability
This online marketplace business model is suitable for platforms with a large number of sellers and a high volume of transactions. It works well for products and services where the value of each transaction is relatively high.
It may not be suitable for niche marketplaces with a low volume of transactions or for products and services with low transaction values. This is because the revenue generated may not cover the costs of operating the marketplace.
Subscription Fee Model
A subscription fee model is one of the most popular marketplace business models.
Benefits
- Recurring fee model: Here, users pay a monthly fee to access services on your platform. Subscription model provides a steady stream of revenue and can be beneficial for platforms that offer value over time.
Examples include platforms like Spotify and YouTube Premium, where users pay a monthly fee for advanced features and capabilities.
Challenges
- Justify continuous value: You must provide continuous value to the customer base to justify the recurring fee. This model may deter users who are unwilling to commit to a subscription.
Suitability
This subscription revenue model is suitable for marketplaces that offer services or products that users need access to over a long period. It is also suitable for platforms that offer premium features or services that enhance the user experience.
Listing Fee Marketplace Model
Under this model, sellers pay a small fee to list their products or services on your marketplace. This option can generate revenue for your platform from the get-go, even before any transactions occur. For example, Etsy and eBay are well-known marketplaces that charge a listing fee from the sellers active on their platforms.
Benefits:
- Immediate Revenue: This model generates revenue for you as soon as a product is listed.
- Low Cost for Sellers: Sellers need to pay only when they list an item on your platform. This helps keep their costs down.
Challenges:
- Barrier for Some Vendors: The upfront listing fee might deter some vendors who are just starting their business or sell infrequently.
- Dependent on Seller Activity: The revenue your platform can make is directly dependent on the number of new listings.
This model is suitable for marketplaces with a large number of sellers who list multiple items and where the cost of listing is justified by the potential sales. However, it may not be suitable for marketplaces with low seller activity or where the items for sale are low value.
Lead Fee Model
The lead fee model is one of the well-known marketplace business models. Here, you charge sellers a flat fee for each lead generated through your platform. Real estate platforms and job marketplaces like Zillow and Upwork often use this marketplace model.
Benefits
- Pay for Performance: Sellers need to pay only when they receive a potential customer lead. This helps overcome their apprehensions about listing on your platform.
- Control Over Costs: Sellers can set a budget for how much they are willing to spend on leads.
Challenges
- Quality of Leads: The main challenge under this model is to ensure the quality of leads, which can affect seller satisfaction.
- Dependent on User Activity: Revenue is dependent on the volume of user activity and engagement on the platform.
Suitability
It is one of the best marketplace business models suitable for platforms where the value of each lead is high and sellers are willing to pay for potential customers. However, a robust system is required to track leads and ensure their quality.
Freemium Model
The freemium model follows a strategy where basic services on the marketplace app are free, but users pay for access to premium features or services. This model is commonly used by software and digital services companies like Dropbox and LinkedIn.
Benefits
- User Acquisition: The free trial period can attract a large user base, some of whom may convert to the paid mode.
- Customer Trust: Users can try the service before committing to a purchase, building trust and improving conversion rates.
Challenges
- Revenue Conversion: Converting free users to paid users can be challenging and requires providing a better value proposition in the premium tier.
- Resource Management: Supporting a large number of free users can strain resources.
Suitability
This model is suitable for marketplaces that offer digital products or services where the cost of supporting additional users is low. However, careful planning is required to balance the needs of free and paid users and ensure a steady revenue stream.
Featured Listings and Ads Model
This is one of the marketplace business models where sellers pay a premium to have their listings prominently displayed or highlighted on your platform. This model is commonly used by marketplaces like Expedia and Indeed, where vendors pay a fee to the platform to display their ads or listings in strategic places.
Benefits
- Increased Visibility for Sellers: Sellers can gain more exposure for their products, potentially leading to new customers to enjoy increased sales.
- Additional Revenue Stream: This model provides an additional source of income for your marketplace, separate from transaction fees.
Challenges
- Balancing User Experience: Too many ads or featured listings can clutter your platform and negatively impact the customer experience.
- Dependent on Seller Investment: The revenue from this model is dependent on sellers’ willingness to pay for featured listings or ads.
Suitability
This model is suitable for marketplaces with a large number of sellers where competition for visibility is high. However, careful management is required to balance the benefits of increased revenue with maintaining a positive user experience.
Mixed Marketplace Business Model
A mixed marketplace business model combines several revenue models to create a diversified income stream. For instance, a marketplace might charge transaction fees and listing fees and offer premium services for a subscription fee. Amazon and Flipkart are prime examples of mixed marketplace business models as they primarily operate on a listing fee model but also offer featured listings and advertising options.
Benefits
- Diversified Revenue Stream: Multiple revenue models can provide a more stable and diversified income for your business.
- Flexibility: This strategy can help maximize your revenue and meet the needs of different types of sellers and buyers.
Challenges
- Complexity: Managing multiple revenue models can be complex and may require more resources on your part to handle different types of transactions.
- Potential Seller Confusion: Some sellers may be deterred from your platform as they can be confused by the multiple fees and charges.
Suitability
This model is suitable for large, established marketplaces that have the resources to manage multiple revenue models and a diverse seller base. However, it may not be suitable for new or small marketplaces due to the complexity of managing multiple revenue streams.
How to Select the Best Marketplace Business Model?
Here are the steps you must follow to select the right option from different marketplace business models:
Step 1: Consider the Market Potential and Competition
Start by evaluating the size, growth potential, and competitive landscape of your target market. Understanding these factors can help you gauge the viability of your marketplace idea.
Step 2: Understand How Your Customers Buy
Analyze your customers’ purchasing behavior and preferences. These insights can help you optimize your marketplace to better meet their needs and expectations.
Step 3: Consider Your Customers’ Needs
Identify the needs and pain points of your audience. Your marketplace should offer solutions to these needs to ensure a unique experiences for customers.
Step 4: Study the Competition
Determine the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors. This competitive intelligence can help you differentiate your marketplace and identify opportunities for innovation.
Step 5: Validate Your Marketplace Idea
Before investing heavily in your marketplace platforms, validate the product/market fit of your idea. This could involve conducting market research, seeking feedback from potential users, and testing your idea with a small audience.
Step 6: Build MVP, Test & Launch the Complete Product
You should start by building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP allows you to test your marketplace idea with real users, gather feedback, and make necessary adjustments before investing heavily in full-scale development. It is a cost-effective and efficient way to ensure your marketplace resonates with your target audience and meets their needs effectively.
Optimizing Marketplace Business Models with Flipkart Commerce Cloud
Choosing the right marketplace business model is a critical step in your journey to launching a successful retail platform. You must have an in-depth understanding of your target market, customer behavior, and competition to be successful in this competitive landscape. Partner with retail technology solution like Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC) to optimize your marketplace performance and set the foundation for sustained growth.
With 15+ years of retail tech experience in building India’s largest retail platform, we offer a suite of custom commerce solutions for budding retailers, including the entire marketplace technology stack, retail media platform solutions, pricing solution, inventory management, and forecasting solutions.
Whether you are launching a new venture or optimizing your existing marketplace, FCC offers all the support you need.
Connect now and start building a marketplace that meets your business goals and delivers an exceptional shopping experience for your customers.
More Blogs
See how retailers and brands are winning with FCC

Mastering Pricing Strategy Framework
Read More
What is a High-Low Pricing Strategy?
Read More
Ultimate Guide To Dynamic Pricing Strategy In 2025
Read More
Retail Pricing Strategies: Winning with Promotion Pricing in Competitive Markets
Read More
Everything About Price Skimming Strategy Explained
Read More
Mastering Pricing Strategy Framework
Read More
What is a High-Low Pricing Strategy?
Read More
Ultimate Guide To Dynamic Pricing Strategy In 2025
Read More
Retail Pricing Strategies: Winning with Promotion Pricing in Competitive Markets
Read More
Everything About Price Skimming Strategy Explained
Read More
Mastering Pricing Strategy Framework
Read More
What is a High-Low Pricing Strategy?
Read More
Ultimate Guide To Dynamic Pricing Strategy In 2025
Read More
Retail Pricing Strategies: Winning with Promotion Pricing in Competitive Markets
Read More